Course 1 Lessons
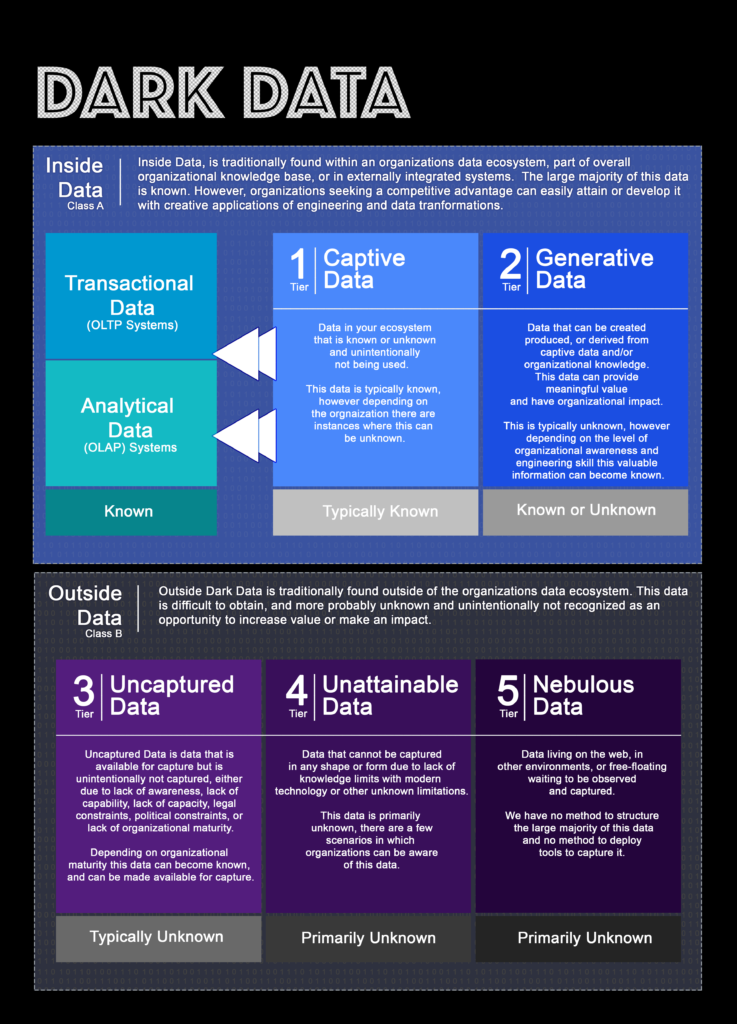
Value-focused Definition of Generative Data:
Data that can be created produced, or derived from
captive data and/or organizational knowledge. This data can provide meaningful value and have organizational impact.
Generative Dark Data
This is typically unknown, however depending on the level of organizational awareness and engineering skill this valuable information can become known.
On the analytical side of an enterprise, a number of systems can enrich and transform both captive and generative data. In the case of near real-time needs for data, event-listening protocols can be put in place to send data directly to data layers that are closer to the data visualization layer. That data then fed back into the traditional OLAP infrastructure for the purpose of storage and future usage. Data marts or data stores are usually the layer that is near the data visualization layer, and they use technologies like Yellowbrick, Hive, Kafka, Tableau, Power BI, Kibana and others to create alerts, dashboards, and other useful intelligence mediums that show what’s going on in their systems and in the market in near real-time. Advanced intelligence and decision-support protocols provide leaders with improved decision-making capabilities.
Inside data in tiers 1 and 2 are typically the easiest and most efficient to use for value creation. This data is often simple to attain and understand. For MVP builds and quick wins tiers one and two are generally the best route to explore first.